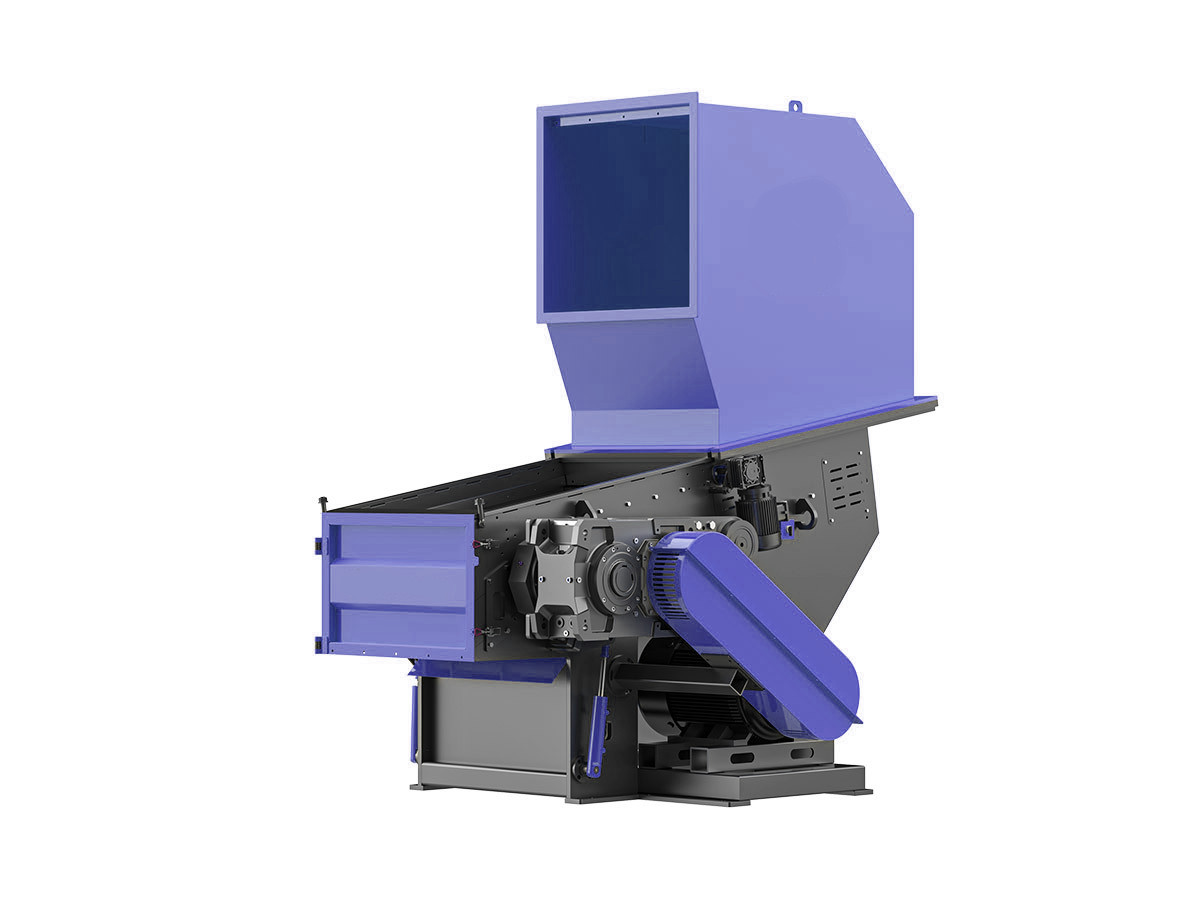
Solid Waste Shredder
Working Principle of Solid Waste Shredder
Solid waste shredders operate using high-torque, low-speed rotating blades that tear, shear, or grind waste materials. The shredding process involves a series of cutting or crushing actions that reduce waste into smaller, uniform pieces.
Most industrial solid waste shredders feature single-shaft, double-shaft, or four-shaft configurations. Single-shaft shredders use a rotating drum with sharp cutters to process waste, while double-shaft shredders use counter-rotating blades to crush and tear materials effectively. Four-shaft shredders further refine waste into finer particles, making them ideal for specialized recycling applications.
Advanced solid waste shredders are equipped with automatic sensors and overload protection to prevent damage from excessive material loads. Some models also feature adjustable output sizes, allowing operators to customize the shredding process according to specific waste processing needs.
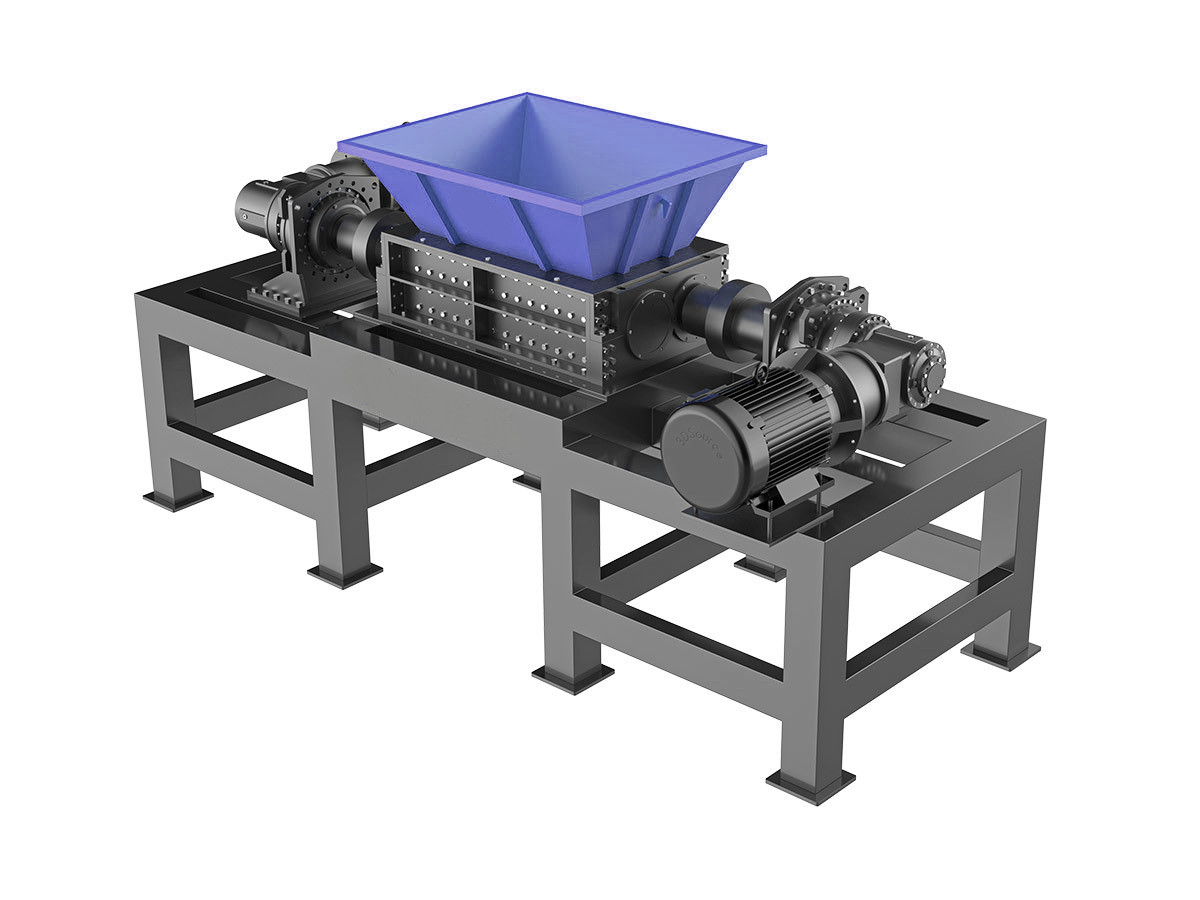

How to Choose the Right Solid Waste Shredder?
Selecting the right solid waste shredder depends on various factors, including the type of waste being processed, desired output size, and processing capacity. Understanding these key considerations helps ensure efficient waste management operations.
1. Identify Waste Material: Different shredders are designed for specific materials. A municipal solid waste shredder is ideal for household and urban waste, while industrial solid waste shredders handle tougher materials like metal scraps, textiles, and construction debris.
2. Determine Shredding Capacity: High-capacity shredders are required for large-scale waste processing, whereas smaller units are suitable for localized or on-site waste management.
3. Consider Cutting Mechanism: Single-shaft shredders offer precise shredding, while double-shaft and four-shaft shredders provide better handling of bulky and high-resistance waste.
4. Evaluate Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient shredders help reduce operational costs while maintaining high-performance shredding.
5. Assess Maintenance Requirements: Easy maintenance and durable blade systems contribute to long-term efficiency and reduced downtime.
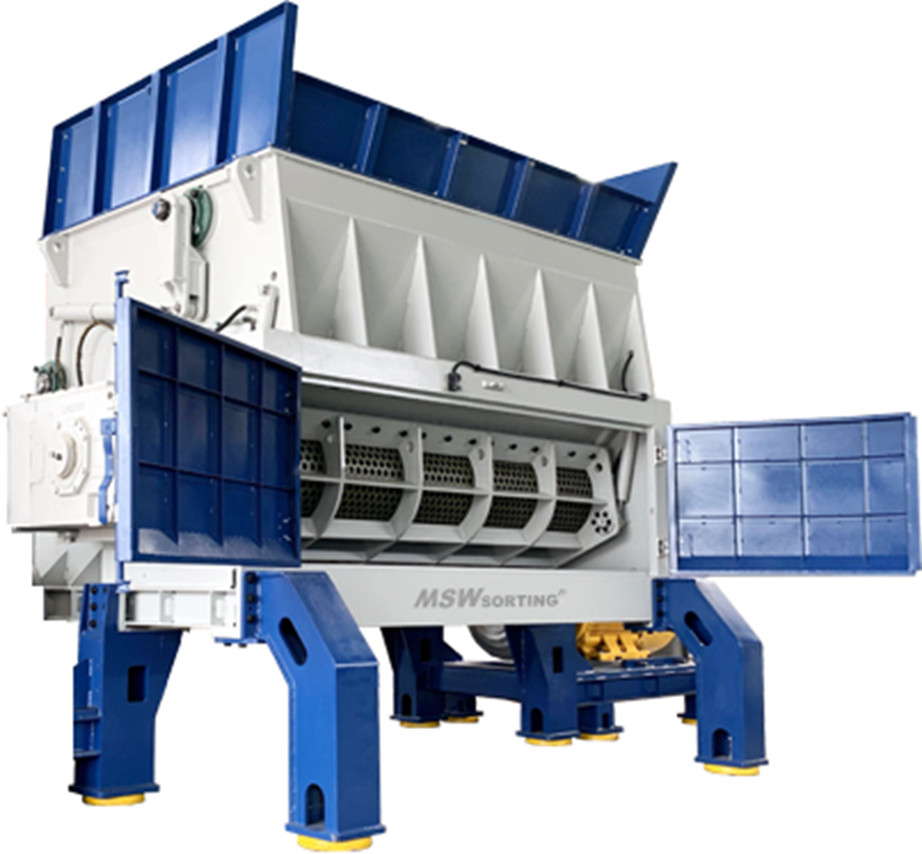

Applications of Solid Waste Shredder
Solid waste shredders are widely used in multiple industries for efficient waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery. Their ability to handle different types of waste makes them essential in various applications.
1. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Processing: Solid waste shredders help manage household waste, reducing the volume of organic and inorganic materials for more efficient waste disposal and recycling.
2. Industrial Waste Management: Factories and manufacturing plants use shredders to process plastic waste, metal scraps, and other industrial byproducts.
3. Recycling Centers: Solid waste shredders play a critical role in breaking down plastics, paper, rubber, and other recyclables into smaller pieces for reprocessing.
4. RDF (Refuse-Derived Fuel) Production: Many solid waste shredders are used to prepare waste for RDF, where non-recyclable materials are converted into fuel for energy generation.
5. Hazardous Waste Disposal: Specialized shredders handle medical waste, chemical containers, and electronic waste, ensuring safe and compliant disposal.
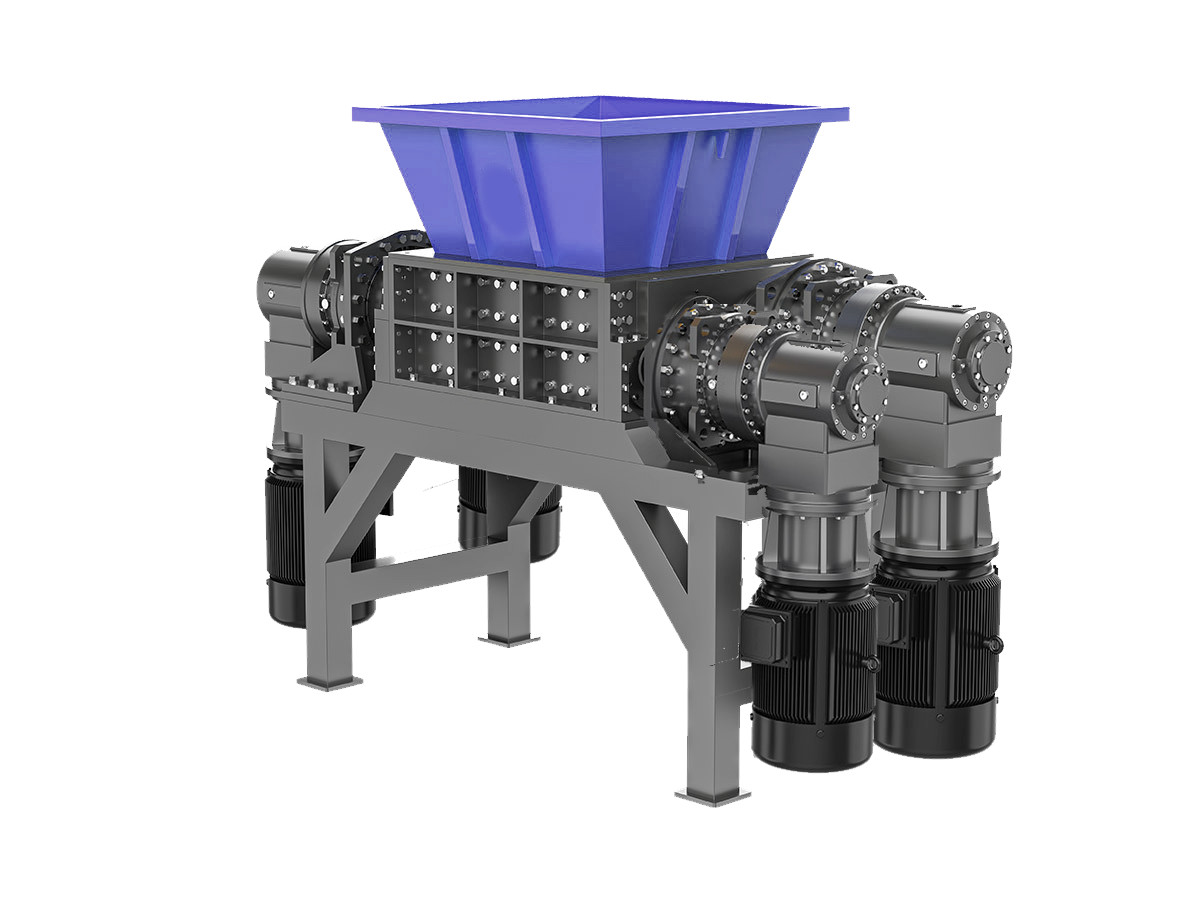

Maintenance of Solid Waste Shredder
Proper maintenance of a solid waste shredder is essential to ensure longevity, efficiency, and consistent performance. Regular inspections and servicing help prevent downtime and costly repairs.
1. Blade Sharpening and Replacement: The cutting blades experience wear over time. Regular sharpening or replacing dull blades ensures optimal shredding efficiency.
2. Lubrication of Moving Parts: Bearings, shafts, and gears should be lubricated periodically to reduce friction and extend the machine's lifespan.
3. Cleaning and Debris Removal: Accumulated debris in the shredding chamber can cause blockages and strain the motor. Routine cleaning prevents unnecessary stress on the machine.
4. Checking Safety Systems: Emergency stop buttons, overload sensors, and other safety features should be tested regularly to maintain a safe operating environment.
5. Scheduled Professional Servicing: Periodic maintenance by professionals ensures that all components are in working condition and helps detect potential issues before they lead to breakdowns.
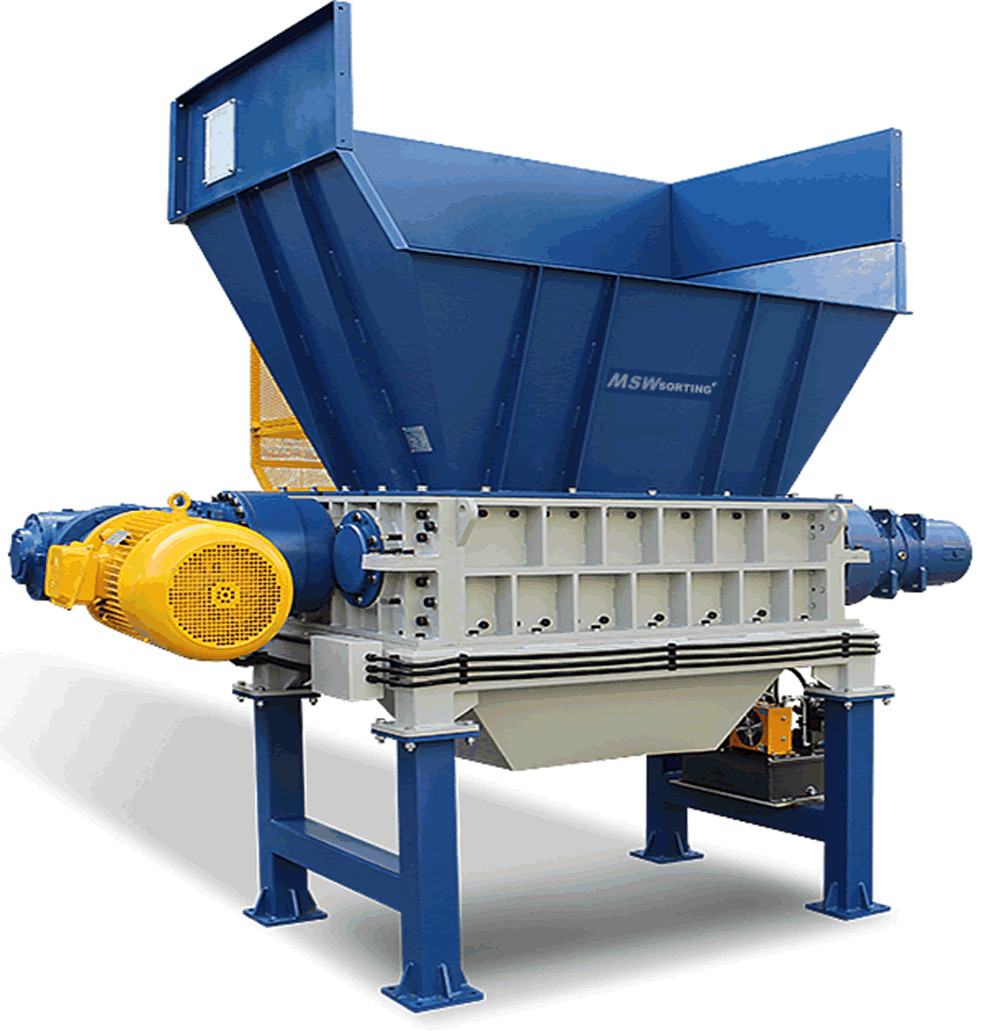

Main Components of Solid Waste Shredder
Solid Waste Shredder Types
Types of Waste Shredder Machine
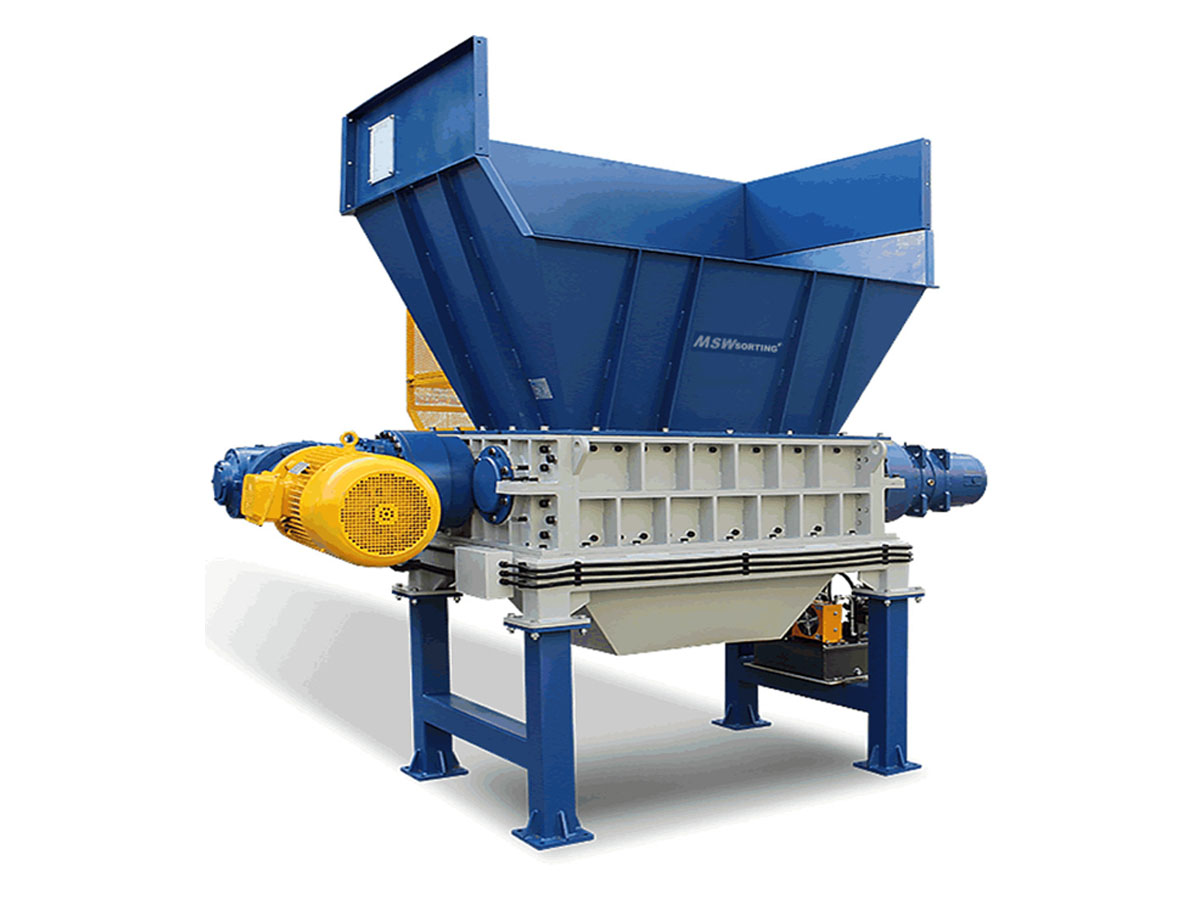

Solid Waste Shredder
Efficiently process municipal and industrial waste into smaller, manageable sizes, aiding in recycling and waste disposal efforts.
Learn more >>

E-Waste Shredder
Specially engineered for electronic waste, this waste shredder handles materials like phones, computers, and circuit boards, ensuring secure disposal and recycling.
Learn more >>

Waste Metal Shredder
Our waste metal shredders efficiently process materials like aluminum, copper, and steel, making it easier to recycle and repurpose metal scrap.
Learn more >>
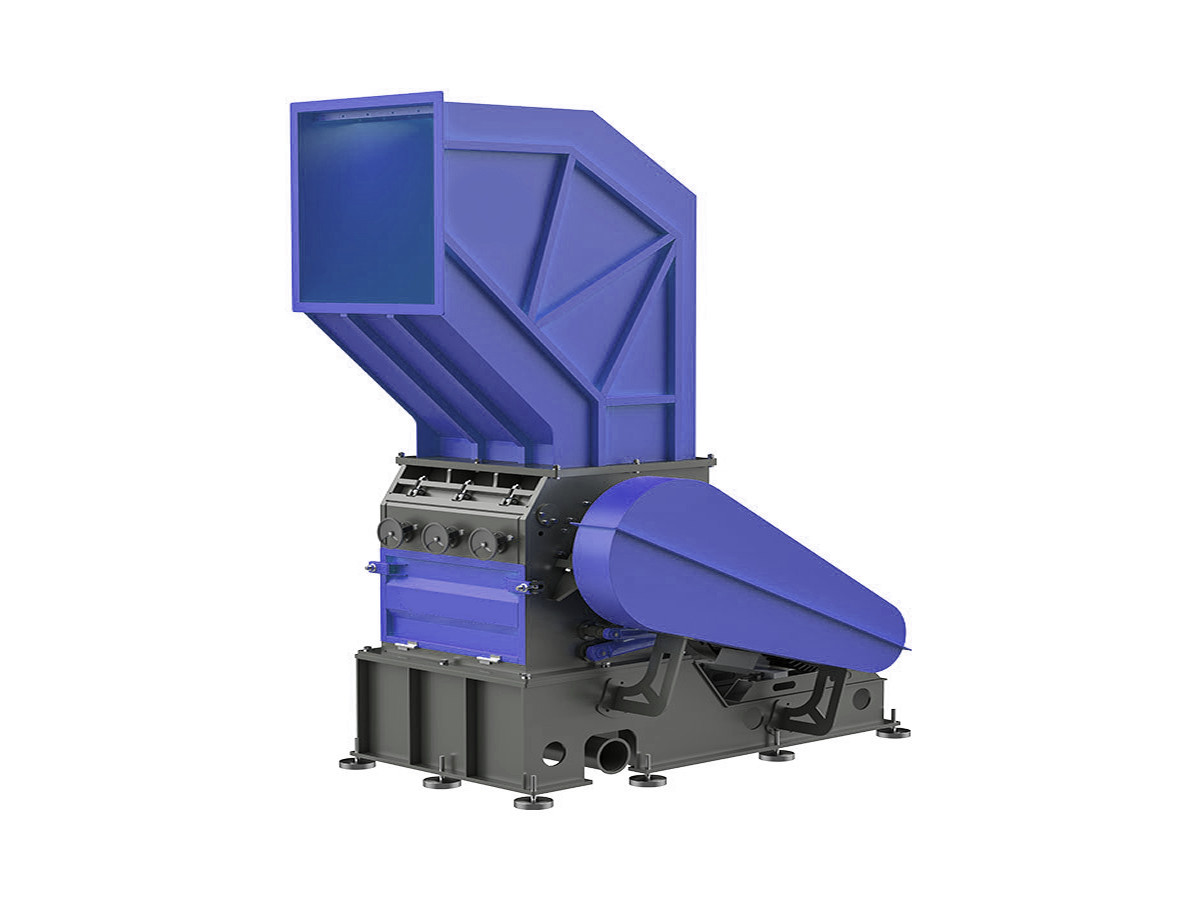
Waste Plastic Shredder
Built for recycling plastics like PE, PP, and PET, this waste shredder helps reduce plastic waste into manageable pieces for further processing.
Learn more >>
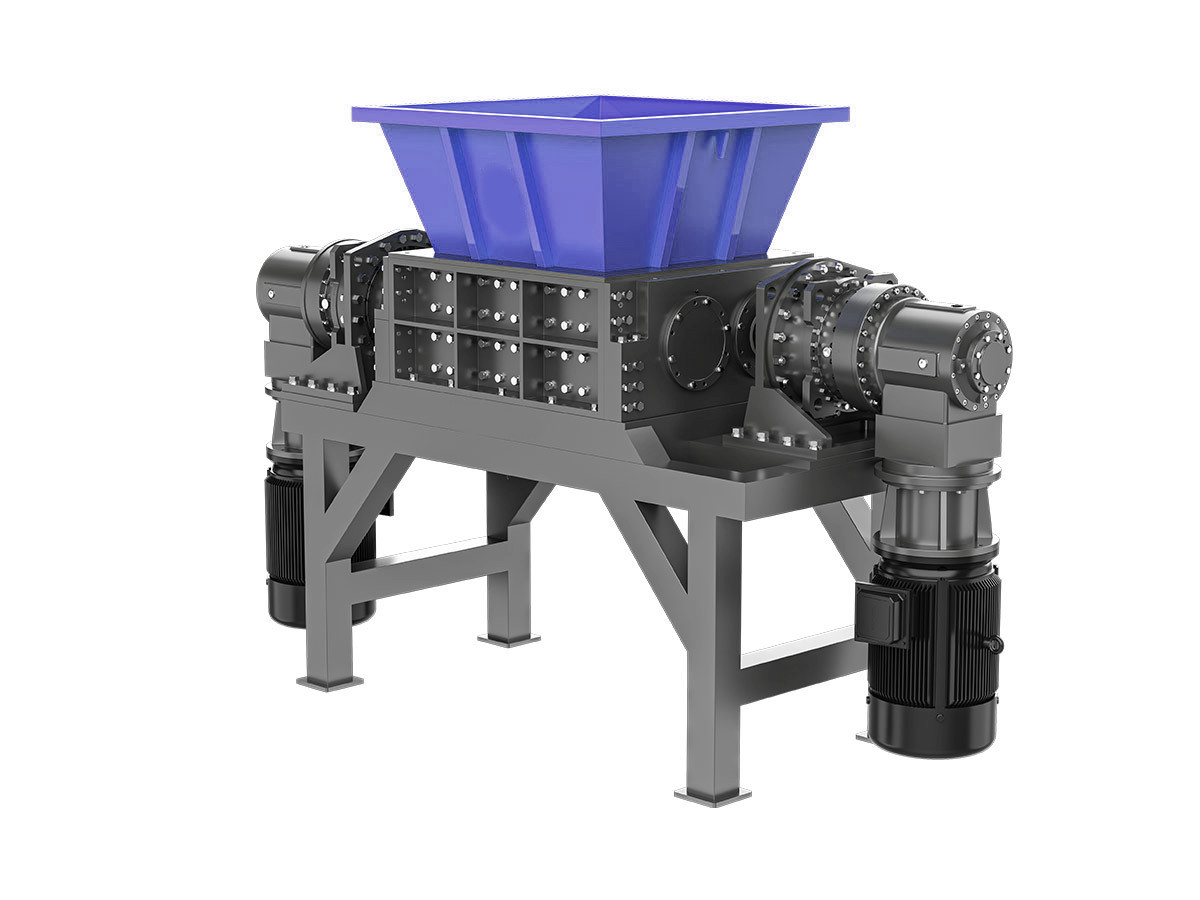

Waste Tire Shredder
Efficiently process used tires into reusable materials, including crumb rubber, for recycling and environmental sustainability.
Learn more >>
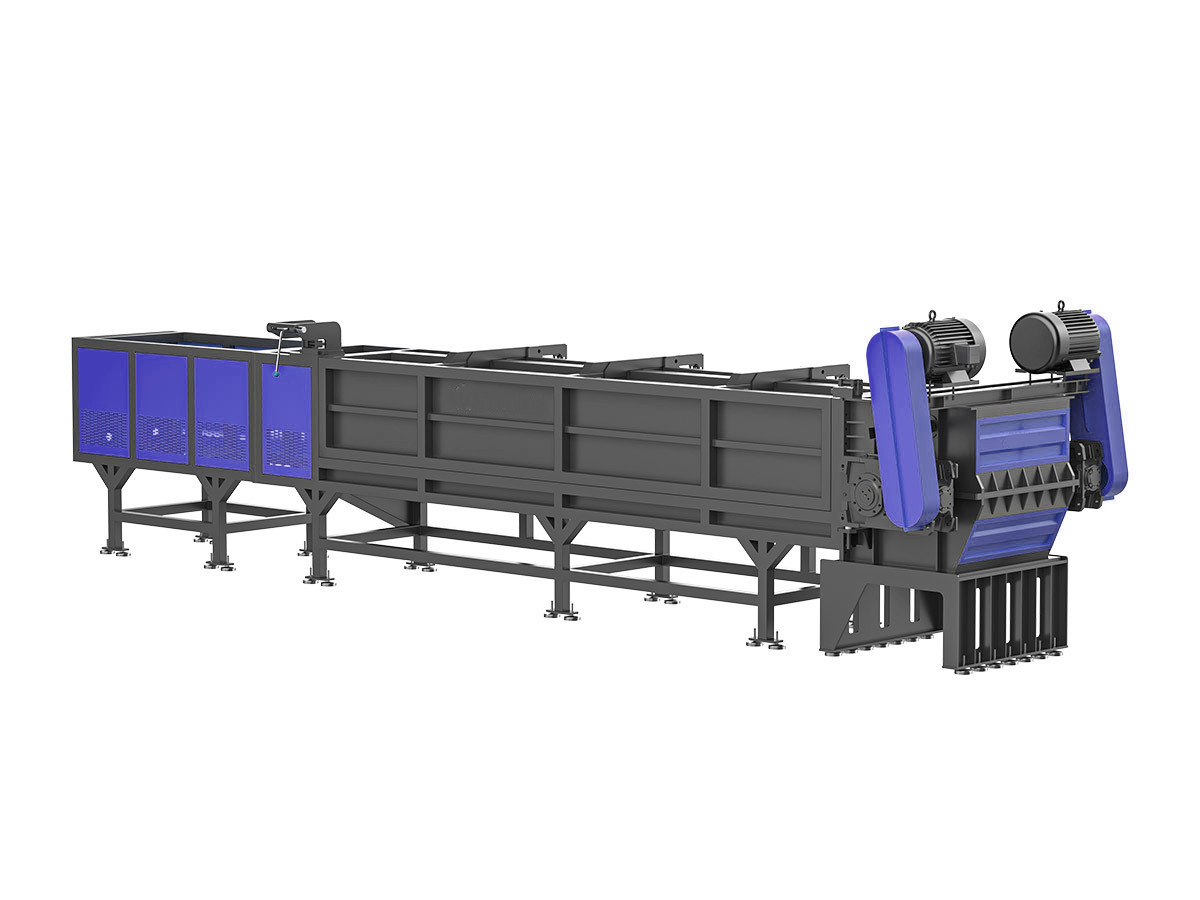

Waste Wood Shredder
Ideal for recycling wood waste like branches, pallets, and wooden furniture, this waste shredder helps create chips, mulch, or compost for eco-friendly disposal.
Learn more >>
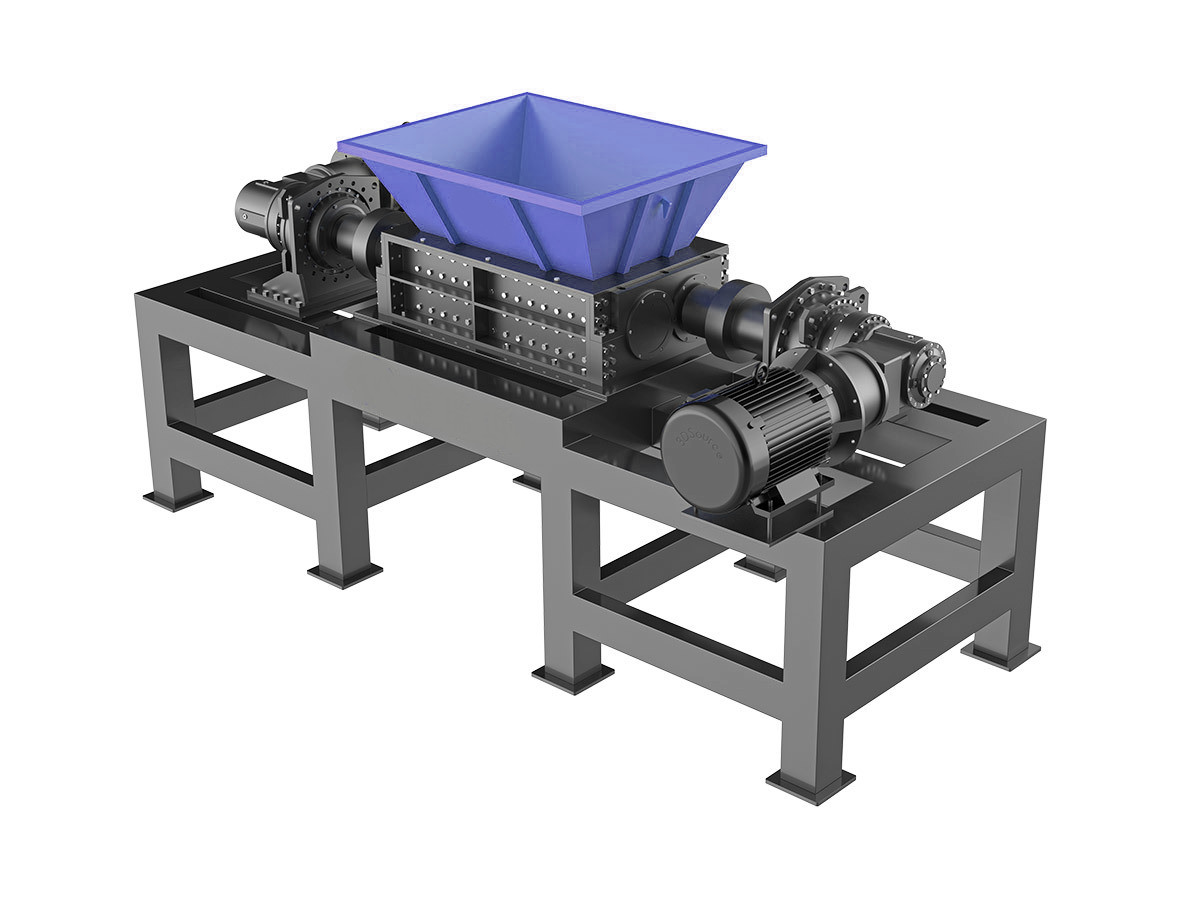

Waste Paper Shredder
Ensure confidential document destruction with our secure waste paper shredders, designed for both small offices and large businesses.
Learn more >>
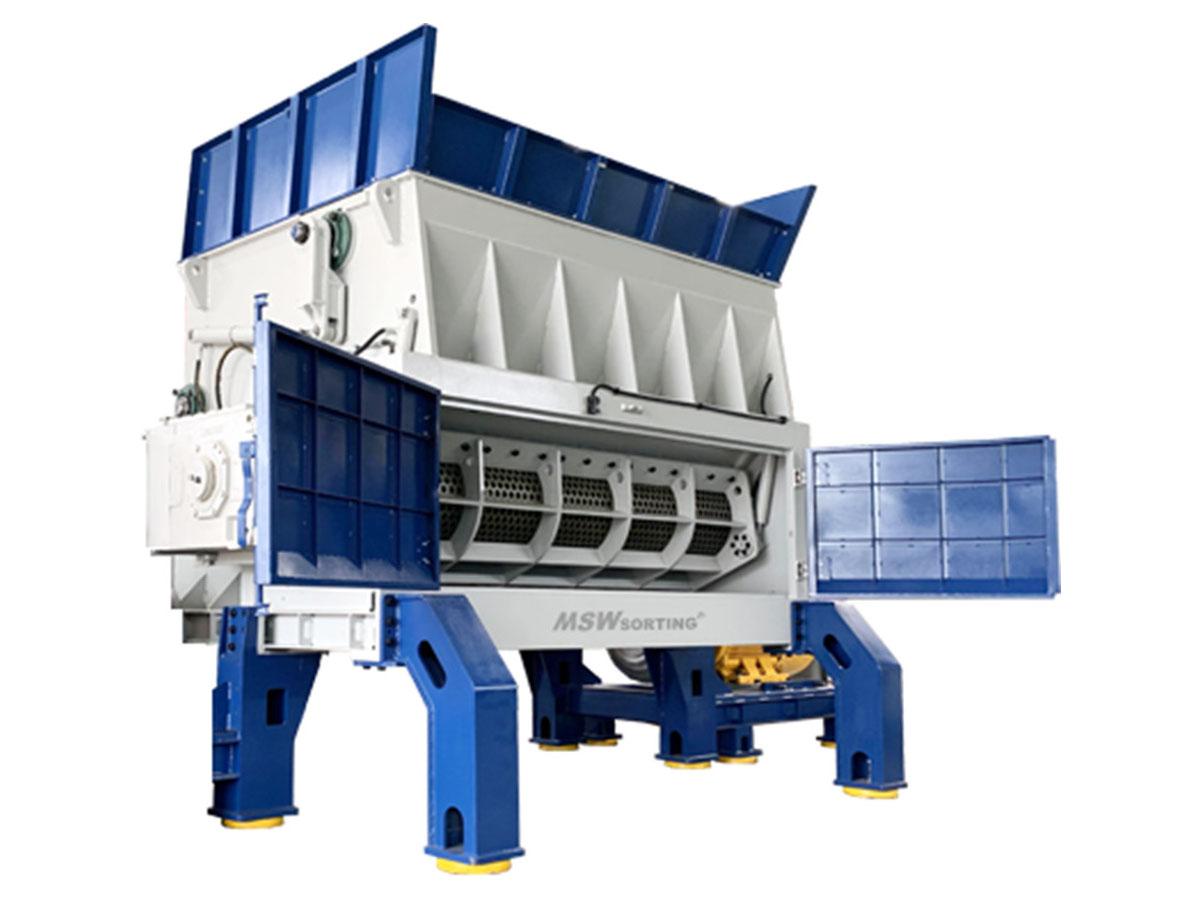

RDF Shredder
Transform waste into refuse-derived fuel (RDF) with this efficient waste shredder, perfect for waste-to-energy applications and reducing landfill dependency.
Learn more >>